What is a Gum Infection?
A gum infection is inflammation and infection of the gums caused by plaque and or/ tartar buildup on teeth. Poor oral hygiene contributes to symptoms like swollen, red gums, bleeding, and bad breath. Untreated, it can progress to severe periodontal disease, risking tooth loss.
Causes
Poor Oral Hygiene
Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to build up, leading to gum inflammation and infection.
Smoking/vaping
Smoking or using tobacco products increases the risk of gum infections and hinders the healing process.
Unhealthy Diet
Diets high in sugars and carbohydrates contribute to plaque formation, fueling gum infections.
Genetics
Genetic factors can influence susceptibility to gum disease, impacting the body’s immune response.
Medical Conditions
Certain health conditions, such as diabetes or immune system disorders, can elevate the risk of gum infections.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, such as during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause, may increase sensitivity to gum inflammation.
Medications
Some medications, like certain high blood pressure medications or antiepileptic medications , may affect oral health and contribute to gum problems.
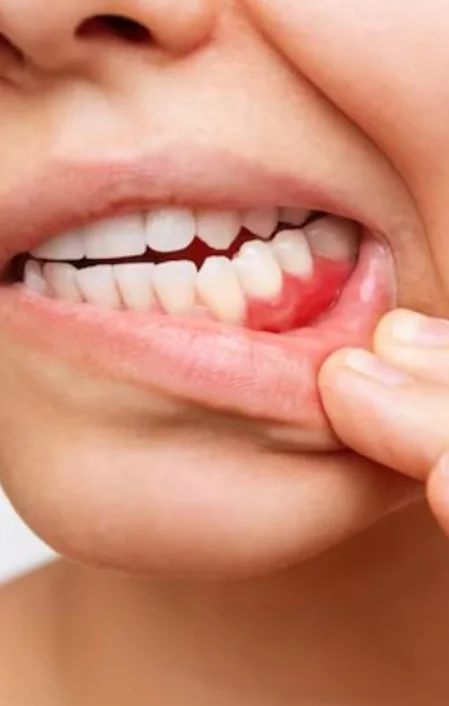
Symptoms
The symptoms of a gum infection, include:
Swollen Gums
Inflammation and puffiness of the gums, especially along the gumline.
Bleeding Gums
Gums that bleed during brushing or flossing, indicating irritation and inflammation.
Red or Purple Gums
Changes in the color of the gums, which may appear redder or purplish instead of a healthy pink.
Sore or tender Gums
Gums that are sensitive to touch or pressure.
Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Persistent bad breath that doesn’t improve with oral hygiene.
Receding Gums
Gums that are pulling away from the teeth, exposing more of the tooth’s surface.
Pus between teeth
The presence of pus or other signs of infection between the teeth and gums.
Changes in tooth alignment
Shifting or loosening of teeth due to weakened gum and bone support.
Sensitive Teeth
Increased sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures.

Prevention
Maintain good oral hygiene
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Use dental floss or interdental brushes daily to clean between teeth.
Healthy lifestyle
- Consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Limit sugary and starchy foods that contribute to plaque formation.
- Avoid smoking and vaping
Regular dental check-ups
Schedule regular dental examinations and cleanings to detect and address potential issues early.
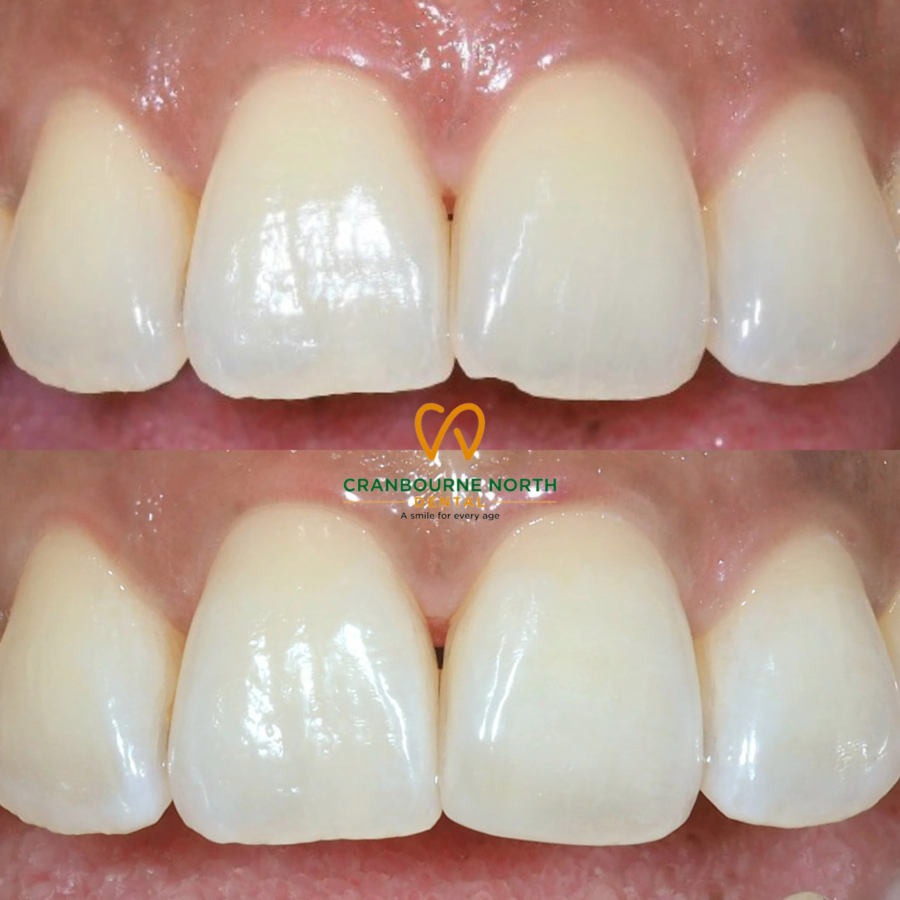
Treatment
Improved oral hygiene
Thorough brushing and flossing to remove plaque and prevent further buildup.
Professional dental cleaning
- Dental cleaning by a dental professional to remove plaque and tartar (hardened plaque) from teeth and gums.
- In cases where significant bone loss accompanies the gum infection, additional intervention for gum treatment may become necessary.
Periodontal maintenance
Regular maintenance appointments to monitor and manage gum health after initial treatment.
Contact Cranbourne North Dental For Gum Infections
If you have infected gums, Cranbourne North Dental can help. Our experienced team will assess your situation, identify the underlying cause, and provide personalised solutions to improve your oral health. Don’t let your infected gums affect your oral health — schedule a consultation with us today and take the first step towards healthier gums.
Our Treatments
Frequently Asked Questions

Do I need antibiotics for my gum infection?
The word infection is almost always associated with Antibiotics. The mouth is a very different place in that for MOST dental infections, systemic Antibiotics (i.e. antibiotic tablets/liquid) are not very effective. The antibiotics are not effective in reaching the source of the infection and if anything, are just a band-aid approach to provide some temporary pain relief. This can be achieved with painkillers so that your body is not unnecessarily exposed to Antibiotics.
Antibiotic resistance is a growing problem and we must be vigilant in our use of Antibiotics.
If there are signs and symptoms of a facial swelling or fever, then antibiotic use may be indicated. Other times may be due to certain pre-disposing medical factors.
Your case will be assessed on an individual basis but do not be surprised if your tooth / gum infection does not need antibiotics.